In recent years, low-carb diets have surged in popularity, capturing the attention of fitness enthusiasts, health professionals, and individuals looking to shed pounds. With promises of quick weight loss and improved health markers, these diets significantly reduce carbohydrate intake in favor of increased protein and fat consumption. But are they the right choice for everyone? In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of low-carb diets, their benefits, and potential drawbacks and help you determine if this dietary approach fits your lifestyle.
Understanding Low-Carb Diets
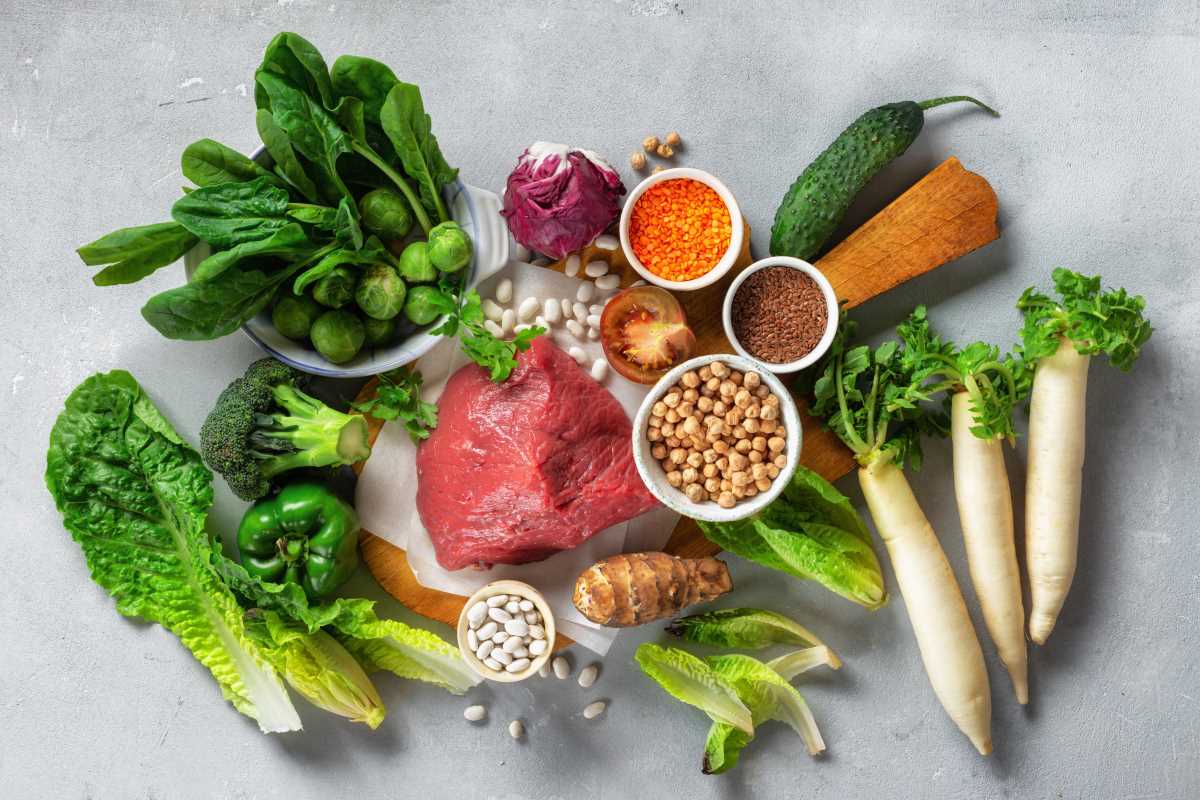
Low-carb diets, as the name suggests, involve significantly reducing the intake of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in foods such as grains (bread, pasta, rice), fruits, vegetables, and sugars, and they are a primary energy source for the body. By limiting these foods and replacing them with protein and fat, low-carb diets aim to shift the body’s metabolism from burning glucose (the sugar derived from carbs) to burning fat for fuel. This metabolic shift is known as ketosis, the hallmark of the ketogenic (keto) diet. Some of the most popular low-carb diets include:
- The Ketogenic Diet (Keto): Extremely low in carbs (usually 20-50 grams of carbs per day) and high in fats, the keto diet encourages the body to enter ketosis, which burns fat for energy instead of glucose.
- The Atkins Diet: Similar to keto but with slightly higher carb intake, especially during the later phases. The diet emphasizes low-carb, high-protein meals to encourage weight loss.
- The Paleo Diet: While not strictly low-carb, the paleo diet eliminates processed foods and emphasizes whole foods, including lean meats, vegetables, fruits, and nuts. It naturally tends to reduce carb intake by avoiding grains and legumes.
The main guiding principle behind low-carb diets is that by lowering carbohydrate consumption, insulin levels drop. This process helps the body to burn stored fat more efficiently, promoting weight loss.
Benefits of Going Low-Carb
- Weight Loss: The most well-known benefit of a low-carb diet is weight loss. The body burns fat for energy rather than glucose by drastically cutting back on carbs. In the initial stages of a low-carb diet, many people experience rapid weight loss due to the reduction in water weight, as carbohydrates bind to water in the body. Over time, fat loss follows as insulin levels remain lower, promoting fat breakdown. Many studies support the effectiveness of low-carb diets for weight loss. They typically result in greater short-term weight loss compared to low-fat diets. Additionally, protein and fat are more satiating than carbohydrates, which helps reduce overall calorie intake by curbing hunger.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: For individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, a low-carb diet can be particularly beneficial. Reducing carbohydrate intake stabilizes blood sugar levels, and insulin sensitivity often improves. Research shows that low-carb diets can significantly reduce the need for medication in people with type 2 diabetes. Low-carb diets help lower blood glucose levels by limiting sugar spikes after meals. As a result, they can be an effective tool for managing or even reversing insulin resistance, which is a precursor to diabetes.
- Heart Health: Some studies have suggested that low-carb diets may improve heart health by lowering certain risk factors such as triglycerides and HDL cholesterol. Reducing carbohydrate intake, particularly refined carbs and sugars, may help lower overall cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, a low-carb diet encourages the consumption of healthier fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, which have been shown to support heart health.
- Reduced Appetite: Another benefit of low-carb diets is their ability to reduce appetite. Eating more protein and fats makes you likely to feel fuller for longer, leading to fewer hunger pangs throughout the day. This effect especially benefits those who struggle with overeating or snacking between meals. High-protein, low-carb meals also help regulate the hormones responsible for hunger, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit and support weight loss efforts.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While low-carb diets offer many benefits but also have potential drawbacks that should be considered before diving in.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: One of the most significant risks of a low-carb diet is the potential for nutritional deficiencies. By cutting out or severely limiting entire food groups like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, you may miss out on essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins (especially vitamin C), and minerals (such as potassium and magnesium). Fiber, for example, is crucial for digestive health and maintaining regular bowel movements, but it is found primarily in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. It’s important to balance your diet with various non-starchy vegetables and nutrient-dense foods to avoid deficiencies. Depending on the type of low-carb diet you follow, you may need to supplement with specific vitamins or minerals.
- Keto Flu: For those following the ketogenic diet, transitioning into ketosis can lead to a temporary condition known as the “keto flu.” This phase occurs as the body adjusts to burning fat instead of carbs for energy. Keto flu symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, dizziness, irritability, nausea, and muscle cramps. These symptoms usually last for a few days to a week and can be alleviated by staying hydrated, replenishing electrolytes, and eating adequate fats.
- Sustainability: While low-carb diets can be effective for weight loss in the short term, their restrictive nature can make them difficult to sustain long-term. Many people find it challenging to adhere to a diet that eliminates entire food groups and significantly reduces their favorite carb-rich foods, such as bread, pasta, and fruits. Over time, this dietary restriction can lead to diet fatigue or even social isolation, as many social gatherings and meals revolve around carb-rich foods. To maintain a low-carb lifestyle, finding ways to make the diet enjoyable and sustainable, such as experimenting with new recipes or allowing occasional indulgences in moderation, is essential.
- Potential Health Risks: Though low-carb diets can benefit many, they also come with potential risks, particularly when followed excessively or improperly. One concern is the **overconsumption of saturated fats**. While fats are a key component of low-carb diets, choosing unhealthy fats like those found in processed meats, butter, and full-fat dairy products can increase cholesterol levels and raise the risk of heart disease. To mitigate this risk, it’s important to focus on healthy fats from sources like olive oil, fatty fish, avocados, and nuts while limiting the intake of processed or red meats.
Who Should Consider a Low-Carb Diet?
Low-carb diets are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They may be particularly beneficial for:
- Individuals aiming to lose weight: Low-carb diets have been shown to promote weight loss by reducing hunger and increasing fat burning.
- People with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome: A low-carb diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Those who prefer higher protein and fat: If you enjoy protein-rich foods or have difficulty feeling full on a typical high-carb diet, a low-carb diet may be easier to stick with.
However, low-carb diets may not be suitable for everyone, especially:
- Athletes or those with high energy demands: Carbohydrates are the body’s primary fuel source for high-intensity exercise, so a low-carb diet may not provide sufficient energy for athletes or individuals who engage in heavy physical activity.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: During pregnancy and lactation, it’s essential to have a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates to support the growing fetus and lactation needs.
- Individuals with kidney issues: Low-carb diets can strain the kidneys more due to increased protein intake, so people with kidney disease or compromised kidney function should consult a healthcare provider before starting a low-carb diet.
Tips for Successfully Adopting a Low-Carb Lifestyle
- Start Gradually: Ease into a low-carb lifestyle by gradually reducing your carb intake. This will help your body adjust and minimize side effects like the keto flu.
- Focus on Quality: Prioritize high-quality, nutrient-dense foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, and plenty of non-starchy vegetables.
- Stay Hydrated: Since low-carb diets can lead to increased water loss, staying hydrated is crucial. Drinking plenty of water and supplementing with electrolytes can help prevent dehydration.
- Monitor Progress: Track your weight, blood sugar levels, and other health markers to assess how the diet affects you.
- Seek Professional Guidance: A nutritionist or dietitian can help you tailor a low-carb plan to meet your individual needs and meet your nutritional requirements.